Notice: Authors are encouraged to submit clinical images for possible publication in the Journal. These may be in any field of Clinical Neurosciences, and should approximately follow the format used here. Please address any submissions to the Assistant Editor, Neurosciences Journal, Prince Sultan Military Medical City, PO Box 7897, Riyadh 11159, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. E-mail: malaskar{at}psmmc.med.sa
Tuberous sclerosis
Clinical Presentation
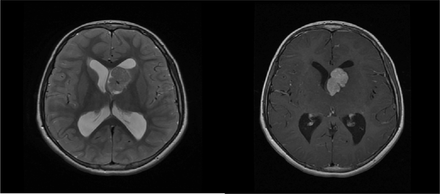
An 11-year-old boy presented to the pediatric neurology clinic for evaluation of seizures. On examination, he has multiple hypopigmented lesions. His brain MRI is shown in Figure 1.
Brain MRI of 11-year-old boy presented to the Pediatric Neurology Clinic for evaluation of seizures.
Questions:
1. What is the name of this lesion?
A. Subependymal nodules.
B. Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
C. Periventricular heterotopia
D. Choroid plexus papilloma
2. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Tuberous sclerosis complex.
B. Neurofibromatosis type 1.
C. Hypomelanosis of Ito.
D. Sturge-Weber syndrome.
3. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the genetics of this disease?
A. It is autosomal dominant with variable penetrance
B. It is autosomal dominant with complete penetrance
C. It can be caused by a mutation in TSC1 gene that encodes for the protein tuberin
D. It can be caused by a mutation in TSC2 gene that encodes for the protein hamartin
4. What is the best management of lesion shown in Figure 1?
A. Anti epileptic drugs
B. Radiotherapy
C. No treatment
D. mTOR inhibitors
5. Which of following is a major criterion for diagnosis of TSC?
A. Meningioma
B. Vestibular schwannoma
C. Subependymal nodules
D. Optic glioma
E. Neurofibroma
Answers & Discussion
1. B
It is a low-grade brain tumor (WHO grade 1) that arise within the ventricles of brain (Foramen of Monro). It is commonly associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). One of major criteria of diagnosis TSC.1
2. A
Tuberous sclerosis complex is a genetic disorder affecting cellular differentiation, proliferation and migration resulting in variety of hamartomatous lesions that may affect every organ system of body.1
3. A
Tuberous sclerosis complex is an autosomal dominant disorder with variable penetrance. Tuberous sclerosis complex is caused either by a mutation in TSC1 gene on chromosome 9 that encodes for protein hamartin or by a mutation in TSC2gene on chromosome 16 that encodes for protein tuberin.2
4. D
Rapamycin and everolimus, an mTOR inhibitors, has been shown to reduce the size of subependymal gaint cell tumors in TSC.3
5. C
Major criteria:
• Angiofibromas (3 or more) or forehead plaque
• Hypomelanotic macules (3 or more)
• Ungual fibromas (2 or more)
• Shagreen patch
• Multiple retinal hamartomas
• Cortical dysplasias (more than 3). This includes tubers and cerebral white matter radial migration lines.
• Subependymal nodule(s)
• Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma(s)
• Cardiac rhabdomyoma
• Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM)
• Angiomyolipomas (2 or more) e common.3
- Copyright: © Neurosciences
Neurosciences is an Open Access journal and articles published are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License (CC BY-NC). Readers may copy, distribute, and display the work for non-commercial purposes with the proper citation of the original work.