Abstract
Objectives: To examine the predictors of pediatric ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt malfunction in a university hospital.
Methods: A retrospective cohort was conducted. Patients under 18 years old who underwent VP shunt revision at least once between 2016 and 2019 were included. Data were stratified based on age, gender, diagnosis, type of valve, valve position, cause of revision, and part revised.
Results: A total of 45 patients (64% males and 36% females) were included in this study. Eighty-two revision surgeries were identified. The most common revised part was the entire shunt system. The most common type of valve which required revision was the low-pressure valve (15.5%). Since a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant, no significant differences among the 4 groups for different points.
Conclusions: Younger age at initial VP shunt insertion is associated with a higher rate of shunt malfunction. Valve mechanical failures followed by infections are the most common causes for the first 3 revisions. A prospective multi-center study to confirm the current findings is recommended.
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt insertion is one of the most common procedures in pediatric neurosurgery for treating hydrocephalus.1 Among pediatric age group hydrocephalus is considered a common, surgically correctable condition in which there is an increase in the volume cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), leading to cerebral ventricles dilatation, thinning of the cerebral mantle, and elevation of intracranial pressure.2 Patients with VP shunts represent more than 30,000 hospital admissions per year.2 Although VP shunting has decreased the morbidity and mortality of hydrocephalus, it is still associated with multiple complications, many of which require surgical revision.1–4 Recent studies have reported the rate of complications following VP shunting to be between 30% and 50%.3⇓⇓–6 Shunt malfunctions causes can be categorized into infectious, mechanical, or functional.2⇓–4 Shunt failure definition is revision or replacement of the original shunt between 30-days and 1-year.2 Mechanical failure can happen at the proximal end, valve, or distal end, and it includes obstruction, disconnection, fracture, distal end migration, or inflammation. Functional failure happens when there is overdrainage or underdrainage of cerebrospinal fluid while the whole shunt system is properly functioning. Infection happens when the patients demonstrate clinical findings and positive fluid sampling results.3 The most common complication necessitating revision are obstruction, infection, and displacement.2,3,6,7 Shunt failure is most common within the first 2 years postoperatively.3 Many important predictors of VP shunt failure have been reported in the literature, including etiologies of the hydrocephalus, prematurity, and age at the initial placement of the shunt.1,8,9 Clinical factors that may increase the risk of shunt revision include time from the first surgery, surgical procedure duration, prior treatments, number of surgeons, surgical expertise, surgical technique, anatomic site of the shunt, and diagnosis.1,7⇓⇓–10 Proximal catheter tip location is another predictor, as tip positions in the Foramen of Monro, lateral ventricles, or the third ventricle all were associated with lower rates of surgical revision.11 Other predictors of shunt failure were reported to be poor catheter placement and use of a non-programmable valve.12
Previous studies have emphasized the need to identify children at risk, and for prospective cohorts to to investigate the relationship of risk factors and incidence of shunt revisions.1,9,10 Risk factors for VP shunt complications vary across institutions and populations, and a very limited number of studies addressing VP shunt malfunction have been conducted in Saudi Arabia, and only one in the last 10 years was published.13
The goal of this study was to determine patterns and predictors of pediatric VP shunt malfunction, causes of the hydrocephalus and VP shunt revision and type of valve malfunction and define the best preventive measures. This knowledge will contribute to lowering the incidence of shunt malfunction, decreasing the number of surgeries, and increasing complication-free intervals between surgeries in hydrocephalic pediatric patients.
Methods
Database creation and literature review
The study was carried out using a retrospective cohort design. Patients below the age of 18 admitted to the neurosurgery ward at King Saud University Medical City for revision of VP shunt from February 2016 to February 2019 were with complete medical records included. The exclusion criteria were conservative, non-surgical management, bilateral VP shunts, VP shunt revision at other institutions, age above 18 years at initial insertion or subsequent revisions, and missed or incomplete documentation.
Information about the revision procedures was collected from the patients’ medical records. A standardized, comprehensive data collection sheet was used to collect patient data, including socio-demographic information, cause of hydrocephalus, date of diagnosis, type of shunt system used, shunt insertion technique, number of previous revisions, and treatment of the primary pathology.
Patients were stratified by age (<6 months, >6 months, 9–12 months, 1–3 years, 3–6 years, >6 years), gender (male and female), diagnosis (congenital hydrocephalus, intracranial tumor, myelomeningocele, aqueductal stenosis, post-traumatic, and post-infectious), hole placement (frontal vs occipital), type of valve (low, medium, high pressure, or programmable), valve position (burr hole: old or new at the revision, in-line), the reason for revision (shunt infection, proximal catheter disconnection, proximal catheter obstruction, distal catheter obstruction, valve mechanical failure, and others), and part revised (whole, proximal, and distal).
The strategies for the literature search were conducted across PUBMED/MEDLINE using the following MeSH search terms: Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt; Pediatrics; Malfunction; Shunt. Searches were tailored using the Boolean operators “AND or OR”. Reference lists of reviews and retrieved articles were assessed for further studies.
Variables and definitions
In our project, shunt system dysfunction was divided into proximal end dysfunction, valve dysfunction, distal end dysfunction, or the entire system dysfunction. Possible causes of revision are mechanical shunt failure or infection.
Mechanical shunt failure was defined by any of the following situations: obstruction of any part by blood, debris, choroid plexus or tissue parenchyma, kinking, adhesions, disconnection, fracture, distal end migration confirmed radiologically or intraoperatively by the surgeon.
Infection was defined by positive clinical findings: high temperature upon presentation, high white blood cell count, or fluid sampling results.
Statistical analysis
Primary variables assessed included age, gender, diagnosis, type of valve, the reason for revision, and part revised. The Kruskall-Wallis test was used to assess the median number of replacements across different groups. No post hoc tests were used due to the p-value indicating no significant relation Data analysis was carried out using IBM SPSS statistical software version 22.0. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Ethical aspects
The hospital ethics committee approved the study protocol. There was no need for informed consent for participation in the study as each participant was represented in the database using an anonymous unique identifier (ID).
Results
A total of 137 patients underwent VP shunt placement at our hospital during the period of this study. These consisted of 80 adults and 57 pediatric cases. Amongst the pediatric cases, 45 had a complete medical record and underwent VP shunt revision and thus were included in the final analysis.
A total of 45 pediatric patients (64% males and 36% females), with a total of 82 revision surgeries were included in the study. The underlying causes of hydrocephalus in the selected sample are shown in Table 1.
Demographic distribution of patients
All the included patients required one or more shunt revisions, 45 (100%). Twenty-one (47%) required revision twice, 11 (24%) required revision 3 times, and 5 (11%) required revision 4 times.
Among the sample, 52% (17% female, 35% male) failed VP shunting within 24 months after initial placement and required revision surgery. The most common age group requiring more than 2 revision surgeries was under 6 months, followed by 1–3 years of age. The causes of VP shunt revisions are illustrated in Table 2.
Causes of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt revision (n=45).
In our sample, the most common surgical revisions involved revising the entire shunt system. The frequency of replaced parts during shunt revisions appears in Table 3. The most common type of valve used at initial insertion was low-pressure (33%), followed by medium-pressure (27%), programmable (20%), and medium-low (13%).
Revised part during shunt revisions
The most common valve requiring revision surgery was the low-pressure valve (15.5%).
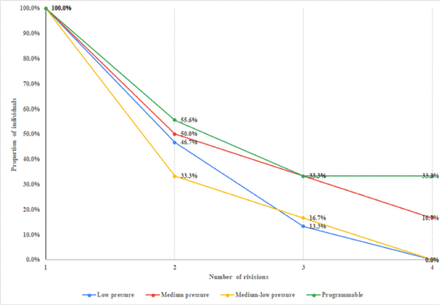
We can see from Table 4 and Figure 1 that low and medium-low pressure valves having one median replacement and medium and programmable valves have a slightly higher number of median revisions. However, this was not shown to be statistically significant. Burr hole location in each revision surgery illustrated in Table 5.
Median number of revisions across different valve types.
Proportion of individuals underwent the valve revisions and corresponding cumulative valve revision frequencies, stratified according to the valve type
Hole placement in revision surgery.
Discussion
Hydrocephalus is a commonly encountered disease in pediatric neurosurgery, managed with VP shunt insertion.1,2 Shunt complications necessitating revisions are common, with revision rates ranging from 30% to 50%.3⇓⇓–6 This study included 45 patients with 82 revision surgeries. The most common age group requiring multiple revision surgeries was under 6 months. In the following section, we will be comparing and contrasting our findings with what is reported in the literature.
Many indications for ventriculoperitoneal shunt revision surgeries have been reported. The most common cause is often mechanical failure, although the specific cause differs, and most studies report the second most common is infection. We report similar results, where valve mechanical failure and infections were found to be the most common indications for the first 3 revisions, with valve mechanical failure accounting for 33%, 19%, and 36% of the first three revisions, respectively. Infection accounted for 24%, 38%, and 27% of the first three, respectively.
Pan P6 retrospectively evaluated risk factors leading to shunt failures in 137 hydrocephalus patients. The most common complications in the cohort were shunt blockade (45.94%), and shunt infection (16.21%). Ahmadvand S, et al7 retrospectively studied 82 patients with 121 revisions, the most common complication reported was obstruction of the shunts (53.6%). Agarwal N et al9 retrospectively studied complications of VP shunt in 41 hydrocephalus patients and 47 complications. Mechanical complications occurred in 33.33%, followed by infective complications (15.63%). Almazroea, A study13 from Saudi Arabia retrospectively studied shunt complications in 65 pediatric patients. Obstruction was the most common cause 38.46% followed by infection 12.3%.
The high probability of failure among the younger age group has been reported by several studies and matches our findings, where we found that the most common age group requiring more than 2 revision surgeries was under 6 months old. Agarwal N et al9 and Tervonen J14 et al studies both reported that the majority of patients who had shunt failure were operated on in the first 2 years of life.
Ahmadvand S et al7 retrospectively studied 30-day shunt failure rate in 82 patients 71% of whom belonged to the pediatrics age group with 121 revisions. The following risk factors were studied: age, gender, household income, level of education, cause of hydrocephalus, causes of revision, type of failure, anatomic site, duration of operation, time of surgery, surgeons’ level of expertise, and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score. Their univariate analysis reported that gender, age, anatomic site, GCS score, surgeons’ level of expertise, and cause of hydrocephalus were significant factors. they also reported proximal catheter to be the main type of shunt failure (70.0%). While our results reported the whole shunt system followed by the valve to be the main types of failure.
Venable GT et al15 reviewed 525 patients with 927 shunt insertion or revision surgeries. They studied risk factors comparing preventable and non-preventable causes. The most common causes for both groups of shunt revision (n=202) were proximal catheter failure 41.6%, followed by valve dysfunction 17.3%, and distal catheter malfunction 13.4%. We report different results where valve mechanical failure and infections were the most common indications for the first 3 revisions, followed by proximal catheter malfunction, accounting for 33% and 24%, and 18% respectively on the first revision.
The most common cause for initial shunt insertion in our study was congenital hydrocephalus in the age group of 0–12 months (38%). Our results are comparable to what was previously reported, where it was reported that congenital hydrocephalus was the most common cause with its rate ranging from 36.5%–47%.6,7
Our study was limited by its retrospective nature and the small sample size, as only patients with a VP shunt revision in our institution with complete detailed documentation in a single institute. We recommend a multi-center study with a larger sample size to confirm the current findings.
In conclusion, higher rate of shunt failure was noted in pediatrics with younger age at initial VP shunt insertion (below 6 months). Valve mechanical failure followed by infections were the most common causes in the first 3 revisions. Revision of the entire shunt system was the most commonly performed procedure 38%. Our results were not consistent with the literature which showed revision of peritoneal (distal) part of the shunt as the most commonly performed procedure. A multi-center study to increase the sample size and confirm the current findings in Saudi Arabia is recommended.
Supplements
* Supplements will be considered for work including proceedings of conferences or subject matter covering an important topic
* Material can be in the form of original work or abstracts.
* Material in supplements will be for the purpose of teaching rather than research.
* The Guest Editor will ensure that the financial cost of production of the supplement is covered.
* Supplements will be distributed with the regular issue of the journal but further copies can be ordered upon request.
* Material will be made available on Saudi Medical Journal website
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank PageCure (https://www.pagecure.com/) for English language editing.
Footnotes
Disclosure. Authors have no conflict of interests, and the work was not supported or funded by any drug company.
- Received March 15, 2020.
- Accepted June 24, 2020.
- Copyright: © Neurosciences
Neurosciences is an Open Access journal and articles published are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License (CC BY-NC). Readers may copy, distribute, and display the work for non-commercial purposes with the proper citation of the original work.