Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate, in a Saudi Arabian context, how the COVID-19 pandemic psychologically impacted persons with multiple sclerosis (PwMS).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was undertaken during the period from October 2021 to March 2022. 738 participants resident in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) completed a self-administered online questionnaire. The research focused on persons diagnosed with MS.
Results: Participant ages spanned from 18 to over 55. The mean was 36.1±12.9 years old. Four hundred eighty-nine (66.3%) of the 738 participants were female. Two hundred sixty-four (35.8%) were single. Four hundred twelve (55.8%) were married. Six hundred eighty-five (92.8%) had received a COVID-19 vaccine. Regarding MS duration, 117 (15.9%) had been diagnosed for less than 2 years, 171 (23.2%) for 2-5 years, while 251 (34%) had the condition for 10 or more years. Regarding psychological health, 11.2% of participants complained of minimal/no depression, 33.3% of mild depression, 28.3% of moderate depression, and 27.1% of moderately severe to severe depression symptoms. Concerning anxiety, 17.2% of participants reported minimal anxiety, 36.9% mild, 23.3% moderate, while 22.6% suffered from severe anxiety symptoms.
Conclusion: A high prevalence of depression and anxiety was found, along with high prevalence of co-occurrence of these disorders among PwMS.
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) was designated by the World Health Organization (WHO) as an infectious disease. The cause of the disease is Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In late 2019, it started spreading around the world. The epicenter was Wuhan, China. The WHO then acknowledged the situation to be a global pandemic on March 11, 2020.1
COVID-19 is extremely contagious and spread via human-to-human transmission. Following the first documented incidence in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), case numbers rapidly increased. To limit the disease’s spread, in response Saudi authorities implemented precautionary measures such as a national lockdown and stay-at-home orders.2
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is defined as an inflammatory disease in the central nervous system (CNS). Effects include diplopia, sensory loss, ocular neuritis, limb weakness, along with cognitive as well as neuropsychiatric dysfunctions.3 Multiple sclerosis is among the world’s most common neurological illnesses. Multiple sclerosis prevalence rate in Saudi Arabia is 40.40/100,000 population, with an estimated projection rate of 61.95/100,000 among Saudi nationals with an average onset during adulthood.4 Multiple sclerosis is also less common among males than females. Moreover, of the 4 clinical forms of MS, the most prevalent is remitting-relapsing MS (RRMS).5 Persons with MS (PwMS) frequently report that they experience psychological problems. In fact, most of those diagnosed experience anxiety, depression, and/or stress.6 Several pre-pandemic studies in the KSA found greater levels of depression, along with significant impacts on quality of life, among MS sufferers.7–11
Compared with age-matched healthy individuals and persons with other chronic illnesses, PwMS had higher levels of anxiety and depression.12 Acute stress is also associated with relapses in PwMS.13 The RRMS sufferers are especially vulnerable to the pandemic’s neuropsychiatric effects.14 Moreover, there is also significant evidence which highlights how acute and psychological stress can trigger an MS relapse.15 Persons with MS are more vulnerable to COVID-19’s economic, social and lifestyle impacts, too. Indeed, due to the pandemic restrictions, PwMS’ critical services were disrupted, terminated, and/or altered.16
No evidence exists that suggests PwMS are more at risk of COVID-19 infection if they are not taking disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) (which may cause severe immune suppression). However, PwMS are at increased risk of burdens and impediments because of COVID-19 restrictions.17 This study therefore aims to evaluate the pandemic’s psychological impact on PwMS in the KSA.
Methods
A study utilizing a cross-sectional method was undertaken in the KSA from October 2021 to March 2022.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was provided by Ha’il University’s Research Ethics Committee (research number: H-2021-186). The research was conducted per the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, concerning studies, which involve human participants.
Study population
The study population comprised persons who had been diagnosed with MS. The inclusion criteria were thus PwMS, who were older than 18 years old, Arabic speakers, and Saudi residents during the COVID-19 pandemic. On the other hand, persons in good health, who had MS but were under 18, and/or lived outside Saudi Arabia during the pandemic, were excluded. Following the application of these criteria, a sample of 738 remained.
Instrument
Participants were considered to have provided informed consent by completing the online questionnaire. The online questionnaire was distributed via social media by the researchers, who received assistance from several nonprofit MS organizations based in Saudi Arabia. Participant anonymity was ensured because names and addresses did not need to be provided.
The questionnaire comprised 5 parts. The first presented the study title and details, so that informed consent could be provided. The second focused on gathering sociodemographic data from participants (age, gender, level of education, occupation, marital status, income, location). The third part concerned participants’ medical backgrounds. The questions asked included whether they had been vaccinated against COVID-19, the date they were diagnosed with MS, what medications they were taking, along with whether they were taking vitamin D.
In the fourth part, participants were asked questions concerning symptoms of depression. These were taken from the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ)-9. This is a valid scale. In turn, Arabic translation was then employed to help screen for depressive symptoms, along with their severity.18,19 The fifth part then asked questions about Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)-7, again using a valid scale, with Arabic translation employed for screening of symptoms.18,20
Data analysis
Data was collected, reviewed, then fed into Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 21 (SPSS: An IBM Company). The statistical methods employed were all 2 tailed. An alpha level of 0.05 was considered significant if the p-value was equal to, or below, 0.05. An overall PHQ-9 score was generated by combining the discrete scores for all items. Scores ranged from 0-27. PHQ-9 scales in the 0-4 range were considered normal. Scores from 5-9 indicated mild depression; 10-14 signified moderate, 15-19 moderately severe, and 20-27 severe. Regarding GAD-7, all items asked respondents to rate their symptom severity for the last 2 weeks. The choices included “not at all”, “several days”, “more than half the days”, and “nearly every day”. Scores of 5, 10, and 15 were the cut-off points for, respectively, mild, moderate, and severe anxiety.
Descriptive analysis was in turn carried out, by prescribing the frequency distribution as well as the percentage for the study variables (respondent bio-demographic data, disease duration, medications). Moreover, prevalence and severity of both anxiety and depression were graphed. Cross tabulation to show distribution of patients’ depression and anxiety by their bio-demographic and other relevant data like vaccination status, disease duration, and medications, was performed, through a Pearson chi-square test for significance, along with an exact probability test for small frequency distributions.
Results
Seven hundred thirty-eight respondents met the inclusion criteria. Ages ranged from 18 to over 55. The mean age was 36.1±12.9 (Table 1).
- Socio-demographic data of MS patients, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Six hundred eighty-five (92.8%) respondents had a COVID-19 vaccine. Regarding MS duration, 117 (15.9%) were diagnosed for under 2 years, 171 (23.2%) for 2-5 years, while 251 (34%) had been diagnosed for over a decade (Table 2).
- Multiple Sclerosis patients characteristic, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
About 11.2% of respondents reported minimal/no depression symptoms, 33.3% mild depression, 28.3% moderate, and 27.1% moderately severe to severe. Seventeen and two percentage reported minimal anxiety levels, 36.9% mild, 23.3% moderate, and 22.6% severe. Overall, just 7.9% of respondents reported no/minimal psychological disorder. Nine and three percentage had depression alone, 3.1% anxiety alone, while 79.7% reported both depression and anxiety symptoms (Table 3).
- Psychological health of MS patients, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Ten and five percentage of those with MS for 2-5 years had normal mental health. This contrasts with 9.4% who had had the disease for under 2 years and 7.2% who had had it for 10 or more years. The recorded statistical significance was p=.026. Ninety and six percentage of non-vaccinated respondents reported depression and anxiety disorders, compared with 78.8% who had been vaccinated (p=.049) (Table 4).
- Relation of MS patients’ diseases duration, vaccination, and medications intake with their psychological health.
We are demonstrating the relation of MS patients sociodemographic data with their psychological health. Significant was found between males and females who had MS, marital status, employment and monthly income (Table 5).
- Relation of MS patients’ socio-demographic data with their psychological health.
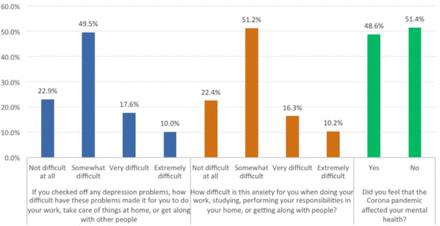
Around 27.6% reported that depression symptoms caused very/extreme difficulty in their day-to-day life, work, and interactions with others (Figure 1).
- Effect of difficulties and covid-19 pandemic on MS patients’ mental health and daily life activities.
Discussion
The rapid global spread of COVID-19 meant that across the world authorities had to implement measures to limit disease transmission within the general population. These preventative measures aimed to protect physical health but had some adverse effects on peoples’ mental health and wellbeing.21–25 PwMS were recognized to have increased susceptibility to mental disorders in research conducted before the pandemic.26,27 This study’s hypothesis was that the COVID-19 pandemic had a negative psychological impact for PwMS.
The study found a high (88.7%) overall prevalence of depression. This is nevertheless below the rate detected in two earlier studies conducted in Saudi Arabia. They recorded depression prevalence of 89.9% and 95.6% among PwMS, respectively.9,10 One explanation for this small reduction in depression prevalence in this study could be the larger – and thus more precise – sample size. Another may be that most of the study population belonged to a MS society which seeks to enhance and improve PwMS’ quality of life.8,28
The COVID-19 pandemic was found in previous research to have a significant negative impact on PwMS’ psychological status.3,29 Moreover, research which evaluated depression levels among PwMS in the initial and peak phases of the pandemic found there to be a significant increase in depression prevalence at the pandemic’s height.30 By contrast, the higher depression prevalence in our sample was inconsistent with multiple studies which found minimal or no change in depression levels among PwMS following the onset of the pandemic, as compared with their baseline depression rate.12,31–33 Interestingly, PwMS who reported anxiety/depression symptoms during the pandemic also reported that their MS symptoms had become worse, too.28 Others again argue that COVID-19 has had a mostly neutral influence on PwMS.34
Regarding anxiety, the study population exhibited a high (82.2%) anxiety rate. A high anxiety rate was also found in Iranian research undertaken very early on during the pandemic.35 High anxiety rates have also been found in Egypt, Iran, and Spain, though the recorded rates were lower than in this research.17,29,36 Despite high anxiety rates among PwMS, significant change in anxiety levels during the pandemic was not found.12,30–33 PwMS who tested positive for COVID-19 and/or faced difficulties attending medical appointments had higher anxiety levels.37
This study also found high levels of co-occurrence of depression and anxiety among PwMS. 79.7% had some degree of both. PwMS, newly diagnosed in the pandemic period, had increased prevalence of depression and anxiety (83.8%) compared with those who had MS for a decade or more (77.7%). Disease duration was in other research not found to impact depression and anxiety rates among PwMS.38 This discrepancy is perhaps because PwMS live with medical uncertainty from the time of diagnosis and thus have experience in dealing with the related discomfort.32,39
The study results did not find that the type of medications used impacted PwMS’ mental health. Past research regarding the behavioral practice of PwMS found that most did not stop taking their medications, though 46% reported experiencing fear and anxiety from taking disease-modifying therapy.40 Younger age has also been associated with the pandemic causing an increased negative psychological impact on PwMS.17,34,41 That said, though there were differences in prevalence rates between age groups, this study found no significant difference in the psychological impact on different age groups. Unvaccinated PwMS were on the other hand found to be significantly more anxious and depressed than those who had received a vaccine(s). Furthermore, PwMS have had good responses to several vaccines.42
The study found females to have a significantly higher prevalence of both depression and anxiety than males. This conforms with the general population.21,22,43 Females with MS have also been found to be more psychologically impacted than their male counterparts in other research.44,45 This study found marital status had a significant impact on PwMS’ mental health, with single persons more prone to depression and anxiety than married or divorced/widowed persons. This contrasts with research undertaken in Iran. This found those who were separated from their partners had higher rates of depressive symptoms.46 Unemployment and lower monthly income were also associated with higher rates of depression and anxiety in the study population. Chinese research also found higher monthly income was linked with less anxiety and depression.47 Interestingly, when our study participants were asked if the pandemic impacted their mental health, most said it had not (51.4%).
Strengths and limitations
This study used a cross-sectional method. Thus, a pre-pandemic baseline rate for depression/anxiety in PwMS, along with psychological impact in general, was not available. This limited the study, as a baseline rate would have helped develop a more precise understanding of the psychological impact of the pandemic on PwMS. Another drawback was that most participants were registered in an MS society which seeks to improve the quality of life of PwMS, which may mean they are not representative of PwMS in general. Moreover, as the study was conducted via an online questionnaire, those who participated may have had more interest in mental health issues than PwMS in general, which again raises questions about the sample’s representativeness.
On the other hand, the study had several strengths. As best the researchers can determine, this is among the first studies in Saudi Arabia to assess the impact of the pandemic on PwMS. It was also the first to specifically assess the psychological impact on PwMS. The sample size is another strength, though there remain difficulties in respect generalizing the study’s findings.
Conclusion
For the global population, the COVID-19 pandemic presented an unprecedented danger. Vulnerable persons and groups were especially impacted, in multiple ways. This study evaluated how the COVID-19 pandemic psychologically impacted PwMS. High rates of anxiety and depression were found. There was also significant co-occurrence of these disorders among PwMS.
Based on the study results, it is recommended that persons diagnosed with MS should be routinely screened for psychiatric disorders. It is also recommended that the treating neurologist encourage PwMS to register to an MS society to help reduce the emotional burden of the disease.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge all the multiple sclerosis patients who participated in this study’s survey. We would like to thank Arfa Multiple Sclerosis Society and their chairman of the board of directors of the association Dr. Fatimah Siyhan Alzahrani for distributing the study survey Among PwMS in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. We would also like to thank Azm Multiple Sclerosis Society for distributing the survey among PwMS in Hail city. The authors would like to thank SHS Academic Services for English language editing.
Footnotes
Disclosure. Authors have no conflict of interests, and the work was not supported or funded by any drug company.
- Received September 4, 2022.
- Accepted January 25, 2023.
- Copyright: © Neurosciences
Neurosciences is an Open Access journal and articles published are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License (CC BY-NC). Readers may copy, distribute, and display the work for non-commercial purposes with the proper citation of the original work.